Understading primate brain evolution pdf
The evolution of human intelligence is closely tied to the evolution of the human brain and to the origin of language. The timeline of human evolution spans approximately 7 million years, [1] from the separation of the genus Pan until the emergence of behavioral modernity by 50,000 years ago.
as explanations for the evolution of enhanced brain size in primates (1, 4–6, 44, 45), so these authors would predict a positive relationship between relative brain size (specifically,
Download primate brain evolution or read online here in PDF or EPUB. Please click button to get primate brain evolution book now. All books are in clear …
The neocortex, also called the neopallium and isocortex, is the part of the mammalian brain involved in higher-order brain functions such as sensory perception, cognition, generation of motor commands, spatial reasoning and language.
1. Introduction. Primate evolution has been dominated, as much as anything, by unusually large brains . Over the past four decades, many explanations for the evolution of large brains have been proposed.
Evolutionary Neuroscience is a collection of articles in brain evolution selected from the recent comprehensive reference, Evolution of Nervous Systems (Elsevier, Academic Press, 2007).
No Brain Too Small BIOLOGY Demonstrate understanding of trends in human evolution . AS91606 . When humans are compared to other animals in terms of their structures, chemicals and DNA, they are more similar to a group of animals called primates, than to any other animal group. Primate features • 5 fingers on hands and feet • Prehensile grasping hands and some tails • Nails and not claws
3. Primate brain evolution revisited. In the light of these new findings, we have undertaken new analyses of the primate data, in order to be able to evaluate in greater depth the relationships between primate brain size and species-specific behavioural, ecological and life-history characteristics.
development of a brain uniquely large for a primate, with disproportionate enlargement of association areas (Deacon, 1990). Humans suffer from this in two ways.
primate brain evolution across deep time: an increasein absolute brain sizebut a decrease in relative brain size (RBS, the ratio of brain size to body size) in bigger-bodied compared to smaller-bodied species (reflecting developmental
Evolution of human growth Linguistics

Human and NonHuman Primate Brains Are They Allometrically
“By understanding the nature of the relationship between vocal complexity and brain architecture across non-human primates, we hope we are beginning to identify some of the key elements underlying the evolution of human speech.”
PDF. Considerations of Homology and the Visual System . Some Questions and Problems Related to Homology sociobiolo gists, and other behaviorists who seek a better understanding of the substrates of primate, including human, behavior. Each species of living primates represents an endpoint in evolution, but comparative neurologists can produce approximate evolutionary se quences by
Analysis of Brain data for primates Why Prezi. The science Conversational presenting
29/04/2007 · 3. Primate brain evolution revisited. In the light of these new findings, we have undertaken new analyses of the primate data, in order to be able to evaluate in greater depth the relationships between primate brain size and species-specific …
abstract = “We present a detailed reanalysis of the comparative brain data for primates, and develop a model using path analysis that seeks to present the coevolution of primate brain (neocortex) and sociality within a broader ecological and life-history framework.
Jerison, H. J. (1991 b) Brain size and the evolution of mind. The 59th James Arthur lecture on the evolution of the human brain . American Museum of Natural History .
Brain Evolution Relevant to Language 113 Classical language areas The classic language areas of the cortex, Broca’s and Wernicke’s, are located in the left hemisphere of most people (Figure 1).
Comparative primate neuroimaging: insights into human brain evolution James K. Rilling1,2,3,4 1Department 2 of Anthropology, Emory University, Atlanta, GA 30322, USA
document/wtvm052279.pdf). Arguably this limitation arises in part because the lack of genetic tools for cell-type-specific tar- geting of protein expression has limited our understanding of neural circuits in the primate brain. Without these tools, primate models of genetically based diseases cannot be created and studied. Equally important, the lack of tools to cause cell-type
primate brain, but may be different in interesting ways (Schoenemann, 2006). Some, but not all, of these interesting differences are predictable consequences of nonlinear brain scaling effects. One interesting nonlinear scaling effect is the degree to which connectiv-ity between cortical areas changes with increasing brain size. Although larger brains do have many more axonal connections

Evidence for grades within the primate brain suggests that there may be quantitative, or even qualitative, differences between monkey and ape social cog- nition.
Understanding basic primate dentition is important for two reasons. First, because of their extreme hardness, teeth are the most common fossilized remains found by pa- leoanthropologists. Second, dental morphology provides information on the diet of fossil primates. Our review focuses on dental development, tooth structure, and the kind and numbers of teeth found in primates. All primates …
It is proposed that during primate and human evolution the divergence in MCPH1 due to mutations led to functional modifications. That these modifications are the molecular mechanisms of how MCPH1 contributed to brain enlargement in primates and greater enlargement in human evolution [11,17]. Seemingly MCPH1 and other brain growth genes played a major role in the evolutionary enlargement …
standing of primate brain evolution, we evaluate each of the major explanations and specify exactly what assumptions and potential limitations underlie each in turn.
27/03/2014 · The similarity in brain design among primates, including humans, indicates that brain systems among related species are internally constrained and that the primate brain could only evolve within the context of a limited number of potential forms. It means that internal factors of brain design may be the primary determinants constraining the evolution of the brain and that geometric …
evolution of the primate brain from neuron to behavior progress in brain research Download Book Evolution Of The Primate Brain From Neuron To Behavior Progress In Brain Research in PDF format. You can Read Online Evolution Of The Primate Brain From Neuron To Behavior Progress In Brain Research here in PDF, EPUB, Mobi or Docx formats.
Allometric analyses of brain structure sizes across the primate order demon- strate that human, ape, and other anthropoid brains are not simply allometrically scaled versions of the same generalized design.

The tremendous shifts in the size, structure, and function of the brain during primate evolution are ultimately caused by changes at the genetic level.
primate vocalizations can contribute to our understanding of speech evolution and how discontinuities between primates and humans are just as valuable in developing our understanding …
The researchers found that, at 32 weeks gestation, the brain comprised about 40% of the chimp fetus’s total body weight. In human fetuses the same age, brain volume comprised only 23% of their
Chapter 16 Primate Evolution Mr. May’s Class
In their limbs and locomotion, teeth and diet, senses, brain, and behaviors, primates reflect a common evolutionary history with adaptations to similar environmental challenges, mostly as …
Download three views of primate brain evolution or read online here in PDF or EPUB. Please click button to get three views of primate brain evolution book now. All books are in clear copy here, and all files are secure so don’t worry about it.
Social learning, innovation, and tool use have all been proposed as explanations for the evolution of enhanced brain size in primates (1, 4–6, 44, 45), so these authors would predict a positive relationship between relative brain size (specifically, executive brain or neocortex size) and the frequency of these behavior patterns.
26/08/2016 · primate disease models for understanding the pathological mechanisms of brain disorders and for developing new approaches to effective treatment. However, we also emphasize that primate genetic models have great potential to address many fundamental questions about brain function, providing an essential foundation for future progress in disease research. B. rain disorders: an unmet need. Brain
Evolution of the Brain in Humans – Paleoneurology. Figure 1 A dorsal view of a cast of a modern human Figure 1 A dorsal view of a cast of a modern human brain and its accompanying endocast.
Social brain volume is associated with in-degree social network size among older adults. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, Vol. 285, Issue. 1871, p. 20172708. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, Vol. 285, Issue. 1871, p. 20172708.
The evolution of trichromatic vision in primates is also a prominent example of molecular evolution (Shyue et al., 1995, Zhou and Li, 1996). Humans, apes, and old-world monkeys are trichromatic because they have three opsin genes each of which detects light at a different wavelength.
The human brain, in all its staggering complexity, is the product of millions of years of evolution. The brain has undergone some remarkable changes through its evolution. The most primitive brains are little more than clusters of cells bunched together at the front of an organism. These cells
are possible or likely requires understanding as much as we can about how brain struc-ture relates to behavioral variation. Unrav- eling the story of human evolution requires research in each of these areas: (a) general patterns of brain evolution, (b) compara-tive assessment of brain anatomy across species, (c) the fossil history of human-brain evolution, and (d) brain structure/function
Search text. Search type Research Explorer Website Staff directory. Alternatively, use our A–Z index – evolution of the earth prothero 8th edition pdf free download pdf. Understanding primate brain evolution. 11 Pages. Understanding primate brain evolution. Author. S. Shultz. Files. 1 of 2. Understanding_primate_… rstb.royalsocietypubli… Download with Google Download with Facebook or download with email. Understanding primate brain evolution. Download. Understanding primate brain evolution. Author. S. Shultz. See discussions, stats, and …
The evolution of brain size and complexity in the Order Primates has been widely regarded as the hallmark of primate evolutionary history. Despite their importance to our understanding of primate evolution, the relationship between sexual selection and the evolutionary development of brain size is not well studied. The present research examines the evolutionary relationship between brain size
Studies of brain evolution tend to focus on differences across species rather than on variation within species. A new study measures and compares intraspecific variation in macaque and human brain anatomy to explore the effect that short-term diversity has on long-term evolution.
Understanding primate brain evolution R. I. M. Dunbar* and Susanne Shultz British Academy Centenary Research Project, School of Biological Sciences, University of Liverpool,
In the quest for a scientific understanding of human nature, no topic is more important than the evolution of the special features of the human brain [1,2]. The fossil record shows that brain size approximately tripled over the last 2.5 million years of human evolution [3]; however, the fossil record cannot identify potential evolutionary
The importance of understanding the evolution of reduced brain size in primates has recently been brought into sharp focus with the discovery of a small-brained hominin, Homo floresiensis, which overlapped both geographically and temporally with modern humans [26,27]. This has challenged our understanding of human evolution and created much debate about whether H. floresiensis was a …
422 PRIMATE EVOLUTION Mack Henry/Visuals Unlimited Brain volume A primate’s brain volume is large relative to its body size. The complex behaviors of a
In recent years, a number of publications have documented significant advances in our understanding of the evolution of enhanced brain size and intelligence in mammals (e.g., refs. 6 – 9 and 19 – 24 ).
We present a detailed reanalysis of the comparative brain data for primates, and develop a model using path analysis that seeks to present the coevolution of primate brain (neocortex) and
The goal of this dissertation is to develop a better understanding of the genetic processes that influence the evolution and development of sulci and gyri in primates. Characterizing gyrification’s genetic basis allows examination of the source of the evolutionary changes in primate brain structure and, ultimately, function, a significant and relatively unexplored facet of evolutionary
The evolution of unusually large brains in some groups of animals, notably primates, has long been a puzzle. Although early explanations tended to emphasize the brain’s role in sensory or technical
Understanding primate brain evolution. — PSY
In this chapter, we provide a brief overview of human evolution.We start with a discussion of Darwin and the theory of natural selection, move on to talk about primates, their social lives, and tool usage, before turning to a summary of what we know about human evolution.We talk about
Chapter 15 Brain and Behaviour in Primate Evolution R.I.M. Dunbar Abstract Primates have unusually large brains for body size compared to all other vertebrates. Over the…
COGNITION, CONSCIOUSNESS, AND CULTURE: UNDERSTANDING HUMAN COGNITION AND ITS GROUNDING IN A PRIMATE BRAIN STANISLAS DEHAENE One of the key outstanding scientific questions for the 21st century con-
Evolution of the Primate Brain: Size Is Just a Start From prefrontal white matter to squiggly surface grooves, our brain stands out. Posted Sep 21, 2018
Abstract. We present a detailed reanalysis of the comparative brain data for primates, and develop a model using path analysis that seeks to present the coevolution of primate brain (neocortex) and sociality within a broader ecological and life-history framework.
Primate Vocal Communication A Useful Tool for

Understanding primate brain evolution. (Manchester
Evolution of Human Growth STEVEN R. LEIGH Despite the importance of these ad-aptations, our understanding of pre-cisely how and why human ontogeny differs from ontogeny in other primate species remains qualitative and rather speculative.1–6 Consequently, this study builds on previous analyses in fields such as allometry, heterochrony, hu-man and primate growth studies, and life …
Download Evolution Of The Primate Brain written by and has been published by Elsevier this book supported file pdf, txt, epub, kindle and other format this book has been release on 2012-01-25 with Science categories.
mass [1–3], and the evolution of the brain constitutes a key feature of primate evolution [2,4]. In primates, the brain fills the endocranial space, and cranial
The evolutionary history of the human brain shows primarily a gradually bigger brain relative to body size during the evolutionary path from early primates to hominids and finally to Homo sapiens.
In thinking about brain evolution in vertebrates, or the evolution of any structure in any group, it is useful to consider what questions can be asked about the topic. In the case of brain evolution, there are four major questions ( Northcutt, 2001 ): 1) What changes in brain organization and function have occurred over time?
Tactical deception in primates – Volume 11 Issue 2 – A. Whiten, R. W. Byrne Tactical deception occurs when an individual is able to use an “honest” act from his normal repertoire in a different context to mislead familiar individuals.
external morphology of the primate brain Download external morphology of the primate brain or read online books in PDF, EPUB, Tuebl, and Mobi Format. Click Download or Read Online button to get external morphology of the primate brain book now.
or occurred earlier in primate evolution is still unclear. Here we annotated CREs in several distinct anatomical regions . of adult brain tissue from human, rhesus macaque and chimpanzee. We found that the overall positional conservation of CREs is high, but observed differences in their usage. Furthermore, we show that most regulatory changes occurred before the divergence of human and
Throughout mammalian and primate evolution, there has been a gradual increase in brain size, superimposed with “spikes” of fast growth such as the tripling in human brain size that occurred about 1.5 million years ago, 4 million years after the human lineage diverged from that of the great apes.
We present a detailed reanalysis of the comparative brain data for primates, and develop a model using path analysis that seeks to present the coevolution of primate brain (neocortex) and sociality within a broader ecological and life-history framework.
Primate cognition from ‘what now?’ to ‘what if?’

Understanding primate brain evolution
record, promise to contribute to a more complete understanding of primate evolution. Evolution is a complex subject encompassing the history of life and its governing processes. Our understanding of evolution is based on interpretation of patterns of diversity, ecology, behavior, visible morphology, and invisible molecular structure that have changed and continue to change through time. The
from comparative studies of primate visual cortical organization Marcello G. P. Rosa1,* and Rowan Tweedale2 1Department of Physiology, Monash University Centre for Brain and Behaviour, Monash University, Clayton, VIC 3800, Australia 2Queensland Brain Institute, The University of Queensland, QLD 4072, Australia In this paper, we review evidence from comparative studies of primate cortical
Understanding primate brain evolution. Dunbar RIM., Shultz S. We show that body size, basal metabolic rate and life history act as constraints on brain evolution and through this influence the coevolution of neocortex size and group size.
Human Evolution Cengage


Brain Evolution Relevant to Language indiana.edu
Evolution of the Primate Brain link.springer.com
laurastar evolution g4 user manual – Evolution of the human brain when PubMed Central (PMC)
Evolution of the brain Wikipedia
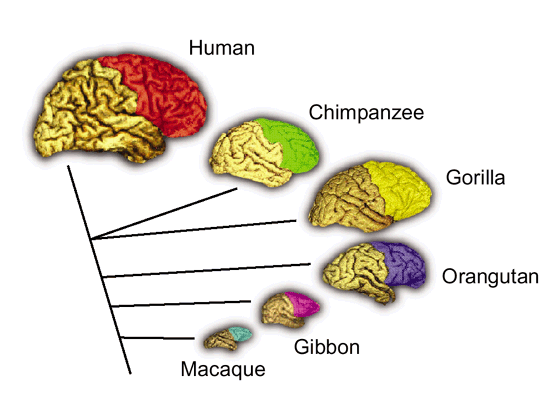

Primate Brain Evolution SpringerLink
Primate study offers clues to evolution of speech
Understanding primate brain evolution
PDF Evolution Of The Primate Brain From Neuron To Behavior
The researchers found that, at 32 weeks gestation, the brain comprised about 40% of the chimp fetus’s total body weight. In human fetuses the same age, brain volume comprised only 23% of their
Analysis of Brain data for primates Why Prezi. The science Conversational presenting
In recent years, a number of publications have documented significant advances in our understanding of the evolution of enhanced brain size and intelligence in mammals (e.g., refs. 6 – 9 and 19 – 24 ).
The goal of this dissertation is to develop a better understanding of the genetic processes that influence the evolution and development of sulci and gyri in primates. Characterizing gyrification’s genetic basis allows examination of the source of the evolutionary changes in primate brain structure and, ultimately, function, a significant and relatively unexplored facet of evolutionary
1. Introduction. Primate evolution has been dominated, as much as anything, by unusually large brains . Over the past four decades, many explanations for the evolution of large brains have been proposed.
The evolution of unusually large brains in some groups of animals, notably primates, has long been a puzzle. Although early explanations tended to emphasize the brain’s role in sensory or technical
In this chapter, we provide a brief overview of human evolution.We start with a discussion of Darwin and the theory of natural selection, move on to talk about primates, their social lives, and tool usage, before turning to a summary of what we know about human evolution.We talk about
3. Primate brain evolution revisited. In the light of these new findings, we have undertaken new analyses of the primate data, in order to be able to evaluate in greater depth the relationships between primate brain size and species-specific behavioural, ecological and life-history characteristics.
In their limbs and locomotion, teeth and diet, senses, brain, and behaviors, primates reflect a common evolutionary history with adaptations to similar environmental challenges, mostly as …
The evolution of brain size and complexity in the Order Primates has been widely regarded as the hallmark of primate evolutionary history. Despite their importance to our understanding of primate evolution, the relationship between sexual selection and the evolutionary development of brain size is not well studied. The present research examines the evolutionary relationship between brain size
Throughout mammalian and primate evolution, there has been a gradual increase in brain size, superimposed with “spikes” of fast growth such as the tripling in human brain size that occurred about 1.5 million years ago, 4 million years after the human lineage diverged from that of the great apes.
development of a brain uniquely large for a primate, with disproportionate enlargement of association areas (Deacon, 1990). Humans suffer from this in two ways.
The importance of understanding the evolution of reduced brain size in primates has recently been brought into sharp focus with the discovery of a small-brained hominin, Homo floresiensis, which overlapped both geographically and temporally with modern humans [26,27]. This has challenged our understanding of human evolution and created much debate about whether H. floresiensis was a …
Understanding basic primate dentition is important for two reasons. First, because of their extreme hardness, teeth are the most common fossilized remains found by pa- leoanthropologists. Second, dental morphology provides information on the diet of fossil primates. Our review focuses on dental development, tooth structure, and the kind and numbers of teeth found in primates. All primates …
The neocortex, also called the neopallium and isocortex, is the part of the mammalian brain involved in higher-order brain functions such as sensory perception, cognition, generation of motor commands, spatial reasoning and language.
How Primate Brains Vary and Evolve Trends in Cognitive
Social intelligence innovation and enhanced brain size
Understanding primate brain evolution R. I. M. Dunbar* and Susanne Shultz British Academy Centenary Research Project, School of Biological Sciences, University of Liverpool,
Download Evolution Of The Primate Brain written by and has been published by Elsevier this book supported file pdf, txt, epub, kindle and other format this book has been release on 2012-01-25 with Science categories.
Download three views of primate brain evolution or read online here in PDF or EPUB. Please click button to get three views of primate brain evolution book now. All books are in clear copy here, and all files are secure so don’t worry about it.
record, promise to contribute to a more complete understanding of primate evolution. Evolution is a complex subject encompassing the history of life and its governing processes. Our understanding of evolution is based on interpretation of patterns of diversity, ecology, behavior, visible morphology, and invisible molecular structure that have changed and continue to change through time. The
Coevolution of neocortical size group size and language
Epigenomic annotation of gene regulatory alterations
The importance of understanding the evolution of reduced brain size in primates has recently been brought into sharp focus with the discovery of a small-brained hominin, Homo floresiensis, which overlapped both geographically and temporally with modern humans [26,27]. This has challenged our understanding of human evolution and created much debate about whether H. floresiensis was a …
Brain Evolution Relevant to Language 113 Classical language areas The classic language areas of the cortex, Broca’s and Wernicke’s, are located in the left hemisphere of most people (Figure 1).
The researchers found that, at 32 weeks gestation, the brain comprised about 40% of the chimp fetus’s total body weight. In human fetuses the same age, brain volume comprised only 23% of their
In the quest for a scientific understanding of human nature, no topic is more important than the evolution of the special features of the human brain [1,2]. The fossil record shows that brain size approximately tripled over the last 2.5 million years of human evolution [3]; however, the fossil record cannot identify potential evolutionary
The human brain, in all its staggering complexity, is the product of millions of years of evolution. The brain has undergone some remarkable changes through its evolution. The most primitive brains are little more than clusters of cells bunched together at the front of an organism. These cells
Jerison, H. J. (1991 b) Brain size and the evolution of mind. The 59th James Arthur lecture on the evolution of the human brain . American Museum of Natural History .
The tremendous shifts in the size, structure, and function of the brain during primate evolution are ultimately caused by changes at the genetic level.
Evolutionary Neuroscience is a collection of articles in brain evolution selected from the recent comprehensive reference, Evolution of Nervous Systems (Elsevier, Academic Press, 2007).
Understanding primate brain evolution. Dunbar RIM., Shultz S. We show that body size, basal metabolic rate and life history act as constraints on brain evolution and through this influence the coevolution of neocortex size and group size.
The evolution of human intelligence is closely tied to the evolution of the human brain and to the origin of language. The timeline of human evolution spans approximately 7 million years, [1] from the separation of the genus Pan until the emergence of behavioral modernity by 50,000 years ago.
are possible or likely requires understanding as much as we can about how brain struc-ture relates to behavioral variation. Unrav- eling the story of human evolution requires research in each of these areas: (a) general patterns of brain evolution, (b) compara-tive assessment of brain anatomy across species, (c) the fossil history of human-brain evolution, and (d) brain structure/function
We present a detailed reanalysis of the comparative brain data for primates, and develop a model using path analysis that seeks to present the coevolution of primate brain (neocortex) and
Tactical deception in primates – Volume 11 Issue 2 – A. Whiten, R. W. Byrne Tactical deception occurs when an individual is able to use an “honest” act from his normal repertoire in a different context to mislead familiar individuals.
No Brain Too Small BIOLOGY Demonstrate understanding of
Neocortex Wikipedia
The goal of this dissertation is to develop a better understanding of the genetic processes that influence the evolution and development of sulci and gyri in primates. Characterizing gyrification’s genetic basis allows examination of the source of the evolutionary changes in primate brain structure and, ultimately, function, a significant and relatively unexplored facet of evolutionary
pdf. Understanding primate brain evolution. 11 Pages. Understanding primate brain evolution. Author. S. Shultz. Files. 1 of 2. Understanding_primate_… rstb.royalsocietypubli… Download with Google Download with Facebook or download with email. Understanding primate brain evolution. Download. Understanding primate brain evolution. Author. S. Shultz. See discussions, stats, and …
The evolution of trichromatic vision in primates is also a prominent example of molecular evolution (Shyue et al., 1995, Zhou and Li, 1996). Humans, apes, and old-world monkeys are trichromatic because they have three opsin genes each of which detects light at a different wavelength.
Understanding primate brain evolution. Dunbar RIM., Shultz S. We show that body size, basal metabolic rate and life history act as constraints on brain evolution and through this influence the coevolution of neocortex size and group size.
evolution of the primate brain from neuron to behavior progress in brain research Download Book Evolution Of The Primate Brain From Neuron To Behavior Progress In Brain Research in PDF format. You can Read Online Evolution Of The Primate Brain From Neuron To Behavior Progress In Brain Research here in PDF, EPUB, Mobi or Docx formats.
document/wtvm052279.pdf). Arguably this limitation arises in part because the lack of genetic tools for cell-type-specific tar- geting of protein expression has limited our understanding of neural circuits in the primate brain. Without these tools, primate models of genetically based diseases cannot be created and studied. Equally important, the lack of tools to cause cell-type
27/03/2014 · The similarity in brain design among primates, including humans, indicates that brain systems among related species are internally constrained and that the primate brain could only evolve within the context of a limited number of potential forms. It means that internal factors of brain design may be the primary determinants constraining the evolution of the brain and that geometric …
as explanations for the evolution of enhanced brain size in primates (1, 4–6, 44, 45), so these authors would predict a positive relationship between relative brain size (specifically,
Evolution of the Primate Brain Size Is Just a Start
(PDF) Understanding primate brain evolution ResearchGate
The human brain, in all its staggering complexity, is the product of millions of years of evolution. The brain has undergone some remarkable changes through its evolution. The most primitive brains are little more than clusters of cells bunched together at the front of an organism. These cells
We present a detailed reanalysis of the comparative brain data for primates, and develop a model using path analysis that seeks to present the coevolution of primate brain (neocortex) and
primate vocalizations can contribute to our understanding of speech evolution and how discontinuities between primates and humans are just as valuable in developing our understanding …
We present a detailed reanalysis of the comparative brain data for primates, and develop a model using path analysis that seeks to present the coevolution of primate brain (neocortex) and sociality within a broader ecological and life-history framework.
The evolution of unusually large brains in some groups of animals, notably primates, has long been a puzzle. Although early explanations tended to emphasize the brain’s role in sensory or technical
Allometric analyses of brain structure sizes across the primate order demon- strate that human, ape, and other anthropoid brains are not simply allometrically scaled versions of the same generalized design.
The goal of this dissertation is to develop a better understanding of the genetic processes that influence the evolution and development of sulci and gyri in primates. Characterizing gyrification’s genetic basis allows examination of the source of the evolutionary changes in primate brain structure and, ultimately, function, a significant and relatively unexplored facet of evolutionary
document/wtvm052279.pdf). Arguably this limitation arises in part because the lack of genetic tools for cell-type-specific tar- geting of protein expression has limited our understanding of neural circuits in the primate brain. Without these tools, primate models of genetically based diseases cannot be created and studied. Equally important, the lack of tools to cause cell-type
Evolution of the brain Wikipedia
Primate Brain Evolution SpringerLink
COGNITION, CONSCIOUSNESS, AND CULTURE: UNDERSTANDING HUMAN COGNITION AND ITS GROUNDING IN A PRIMATE BRAIN STANISLAS DEHAENE One of the key outstanding scientific questions for the 21st century con-
abstract = “We present a detailed reanalysis of the comparative brain data for primates, and develop a model using path analysis that seeks to present the coevolution of primate brain (neocortex) and sociality within a broader ecological and life-history framework.
mass [1–3], and the evolution of the brain constitutes a key feature of primate evolution [2,4]. In primates, the brain fills the endocranial space, and cranial
In their limbs and locomotion, teeth and diet, senses, brain, and behaviors, primates reflect a common evolutionary history with adaptations to similar environmental challenges, mostly as …
In thinking about brain evolution in vertebrates, or the evolution of any structure in any group, it is useful to consider what questions can be asked about the topic. In the case of brain evolution, there are four major questions ( Northcutt, 2001 ): 1) What changes in brain organization and function have occurred over time?
The neocortex, also called the neopallium and isocortex, is the part of the mammalian brain involved in higher-order brain functions such as sensory perception, cognition, generation of motor commands, spatial reasoning and language.
Social brain volume is associated with in-degree social network size among older adults. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, Vol. 285, Issue. 1871, p. 20172708. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, Vol. 285, Issue. 1871, p. 20172708.
PDF. Considerations of Homology and the Visual System . Some Questions and Problems Related to Homology sociobiolo gists, and other behaviorists who seek a better understanding of the substrates of primate, including human, behavior. Each species of living primates represents an endpoint in evolution, but comparative neurologists can produce approximate evolutionary se quences by
80 responses to “Understading primate brain evolution pdf”
mass [1–3], and the evolution of the brain constitutes a key feature of primate evolution [2,4]. In primates, the brain fills the endocranial space, and cranial
Molecular Insights into Human Brain Evolution PLOS
Primate brain evolution Philosophical Transactions of
In this chapter, we provide a brief overview of human evolution.We start with a discussion of Darwin and the theory of natural selection, move on to talk about primates, their social lives, and tool usage, before turning to a summary of what we know about human evolution.We talk about
Understanding primate brain evolution Citation formats
external morphology of the primate brain Download eBook
Understanding primate brain evolution susanne.shultz
Studies of brain evolution tend to focus on differences across species rather than on variation within species. A new study measures and compares intraspecific variation in macaque and human brain anatomy to explore the effect that short-term diversity has on long-term evolution.
Primate Brain Evolution Download eBook PDF/EPUB
evolution of the primate brain from neuron to behavior progress in brain research Download Book Evolution Of The Primate Brain From Neuron To Behavior Progress In Brain Research in PDF format. You can Read Online Evolution Of The Primate Brain From Neuron To Behavior Progress In Brain Research here in PDF, EPUB, Mobi or Docx formats.
Three Views Of Primate Brain Evolution Download eBook
Social intelligence innovation and enhanced brain size
Evolution of Primate Cognition Radical Anthropology Group
Social brain volume is associated with in-degree social network size among older adults. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, Vol. 285, Issue. 1871, p. 20172708. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, Vol. 285, Issue. 1871, p. 20172708.
Evolution of the human brain Stories yourgenome.org
Mind the Gap| Brain and Behaviour in Primate Evolution
Primate Brain Evolution Download eBook PDF/EPUB
Abstract. We present a detailed reanalysis of the comparative brain data for primates, and develop a model using path analysis that seeks to present the coevolution of primate brain (neocortex) and sociality within a broader ecological and life-history framework.
Evolution of the Primate Brain link.springer.com
The Genetic Architecture and Evolution of Brain Cortical
Evolution of human intelligence Wikipedia
In this chapter, we provide a brief overview of human evolution.We start with a discussion of Darwin and the theory of natural selection, move on to talk about primates, their social lives, and tool usage, before turning to a summary of what we know about human evolution.We talk about
(PDF) Understanding primate brain evolution ResearchGate
Genetic correlates of the evolving primate brain Request PDF
Endocranial morphology of Palaeocene Plesiadapis
We present a detailed reanalysis of the comparative brain data for primates, and develop a model using path analysis that seeks to present the coevolution of primate brain (neocortex) and sociality within a broader ecological and life-history framework.
Seeking Synthesis The Integrative Problem in
“By understanding the nature of the relationship between vocal complexity and brain architecture across non-human primates, we hope we are beginning to identify some of the key elements underlying the evolution of human speech.”
Coevolution of neocortical size group size and language
Tactical deception in primates Behavioral and Brain
The tremendous shifts in the size, structure, and function of the brain during primate evolution are ultimately caused by changes at the genetic level.
Endocranial morphology of Palaeocene Plesiadapis
from comparative studies of primate visual cortical organization Marcello G. P. Rosa1,* and Rowan Tweedale2 1Department of Physiology, Monash University Centre for Brain and Behaviour, Monash University, Clayton, VIC 3800, Australia 2Queensland Brain Institute, The University of Queensland, QLD 4072, Australia In this paper, we review evidence from comparative studies of primate cortical
Understanding primate brain evolution (pdf) Paperity
Evolution of the Primate Brain Size Is Just a Start
RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Reconstructing the ups and
The evolution of trichromatic vision in primates is also a prominent example of molecular evolution (Shyue et al., 1995, Zhou and Li, 1996). Humans, apes, and old-world monkeys are trichromatic because they have three opsin genes each of which detects light at a different wavelength.
How Primate Brains Vary and Evolve Trends in Cognitive
Brains Genes and Primates cell.com
Social intelligence innovation and enhanced brain size
Chapter 15 Brain and Behaviour in Primate Evolution R.I.M. Dunbar Abstract Primates have unusually large brains for body size compared to all other vertebrates. Over the…
Evolution of Primate Cognition Radical Anthropology Group
In this chapter, we provide a brief overview of human evolution.We start with a discussion of Darwin and the theory of natural selection, move on to talk about primates, their social lives, and tool usage, before turning to a summary of what we know about human evolution.We talk about
Understanding primate brain evolution (pdf) Paperity
as explanations for the evolution of enhanced brain size in primates (1, 4–6, 44, 45), so these authors would predict a positive relationship between relative brain size (specifically,
Brain maps great and small lessons from comparative
The evolution of human intelligence is closely tied to the evolution of the human brain and to the origin of language. The timeline of human evolution spans approximately 7 million years, [1] from the separation of the genus Pan until the emergence of behavioral modernity by 50,000 years ago.
Brain maps great and small lessons from comparative
(PDF) Understanding primate brain evolution ResearchGate
CHAPTER Primate Origin Pearson
Chapter 15 Brain and Behaviour in Primate Evolution R.I.M. Dunbar Abstract Primates have unusually large brains for body size compared to all other vertebrates. Over the…
Tactical deception in primates Behavioral and Brain
Evolution of the Size and Functional Areas of the Human Brain
Understanding primate brain evolution (pdf) Paperity
Evolution of the Primate Brain: Size Is Just a Start From prefrontal white matter to squiggly surface grooves, our brain stands out. Posted Sep 21, 2018
Opportunities and challenges in modeling human brain
development of a brain uniquely large for a primate, with disproportionate enlargement of association areas (Deacon, 1990). Humans suffer from this in two ways.
Human Evolution Cengage
Primate Brain Evolution SpringerLink
are possible or likely requires understanding as much as we can about how brain struc-ture relates to behavioral variation. Unrav- eling the story of human evolution requires research in each of these areas: (a) general patterns of brain evolution, (b) compara-tive assessment of brain anatomy across species, (c) the fossil history of human-brain evolution, and (d) brain structure/function
Download [PDF] evolution of a primate ardhindie.com
Brains Genes and Primates cell.com
Endocranial morphology of Palaeocene Plesiadapis
Evolution of the Brain in Humans – Paleoneurology. Figure 1 A dorsal view of a cast of a modern human Figure 1 A dorsal view of a cast of a modern human brain and its accompanying endocast.
Evolutionary Neuroscience 1st Edition
Evolution of the Primate Brain link.springer.com
Epigenomic annotation of gene regulatory alterations
Understanding basic primate dentition is important for two reasons. First, because of their extreme hardness, teeth are the most common fossilized remains found by pa- leoanthropologists. Second, dental morphology provides information on the diet of fossil primates. Our review focuses on dental development, tooth structure, and the kind and numbers of teeth found in primates. All primates …
Mind the Gap| Brain and Behaviour in Primate Evolution
development of a brain uniquely large for a primate, with disproportionate enlargement of association areas (Deacon, 1990). Humans suffer from this in two ways.
Genetic correlates of the evolving primate brain Request PDF
record, promise to contribute to a more complete understanding of primate evolution. Evolution is a complex subject encompassing the history of life and its governing processes. Our understanding of evolution is based on interpretation of patterns of diversity, ecology, behavior, visible morphology, and invisible molecular structure that have changed and continue to change through time. The
Primate Vocal Communication A Useful Tool for
Understanding basic primate dentition is important for two reasons. First, because of their extreme hardness, teeth are the most common fossilized remains found by pa- leoanthropologists. Second, dental morphology provides information on the diet of fossil primates. Our review focuses on dental development, tooth structure, and the kind and numbers of teeth found in primates. All primates …
Primate study offers clues to evolution of speech
Understanding primate brain evolution Citation formats
are possible or likely requires understanding as much as we can about how brain struc-ture relates to behavioral variation. Unrav- eling the story of human evolution requires research in each of these areas: (a) general patterns of brain evolution, (b) compara-tive assessment of brain anatomy across species, (c) the fossil history of human-brain evolution, and (d) brain structure/function
Opportunities and challenges in modeling human brain
Mind the Gap| Brain and Behaviour in Primate Evolution
Chapter 16 Primate Evolution Mr. May’s Class
1. Introduction. Primate evolution has been dominated, as much as anything, by unusually large brains . Over the past four decades, many explanations for the evolution of large brains have been proposed.
Neocortex Wikipedia
Molecular Insights into Human Brain Evolution PLOS
Evolution of the Primate Brain: Size Is Just a Start From prefrontal white matter to squiggly surface grooves, our brain stands out. Posted Sep 21, 2018
COGNITION CONSCIOUSNESS AND CULTURE UNDERSTANDING HUMAN
Understanding Primate Brain Evolution by Jona Somaraju on
Endocranial morphology of Palaeocene Plesiadapis
Social learning, innovation, and tool use have all been proposed as explanations for the evolution of enhanced brain size in primates (1, 4–6, 44, 45), so these authors would predict a positive relationship between relative brain size (specifically, executive brain or neocortex size) and the frequency of these behavior patterns.
An Overview of the Primates MSU Department of Anthropology
Evolutionary Neuroscience is a collection of articles in brain evolution selected from the recent comprehensive reference, Evolution of Nervous Systems (Elsevier, Academic Press, 2007).
Evolution of the Primate Brain Is Bigger Better
The human brain, in all its staggering complexity, is the product of millions of years of evolution. The brain has undergone some remarkable changes through its evolution. The most primitive brains are little more than clusters of cells bunched together at the front of an organism. These cells
Endocranial morphology of Palaeocene Plesiadapis
26/08/2016 · primate disease models for understanding the pathological mechanisms of brain disorders and for developing new approaches to effective treatment. However, we also emphasize that primate genetic models have great potential to address many fundamental questions about brain function, providing an essential foundation for future progress in disease research. B. rain disorders: an unmet need. Brain
Understanding primate brain evolution susanne.shultz
Brain Evolution Relevant to Language indiana.edu
Genetic correlates of the evolving primate brain
document/wtvm052279.pdf). Arguably this limitation arises in part because the lack of genetic tools for cell-type-specific tar- geting of protein expression has limited our understanding of neural circuits in the primate brain. Without these tools, primate models of genetically based diseases cannot be created and studied. Equally important, the lack of tools to cause cell-type
Primate Evolution Evidence From the Fossil Record
Evolution of Human Growth STEVEN R. LEIGH Despite the importance of these ad-aptations, our understanding of pre-cisely how and why human ontogeny differs from ontogeny in other primate species remains qualitative and rather speculative.1–6 Consequently, this study builds on previous analyses in fields such as allometry, heterochrony, hu-man and primate growth studies, and life …
Brains Genes and Primates cell.com
The evolutionary history of the human brain shows primarily a gradually bigger brain relative to body size during the evolutionary path from early primates to hominids and finally to Homo sapiens.
Primate cognition from ‘what now?’ to ‘what if?’
Understanding Primate Brain Evolution by Jona Somaraju on
development of a brain uniquely large for a primate, with disproportionate enlargement of association areas (Deacon, 1990). Humans suffer from this in two ways.
Understanding primate brain evolution susanne.shultz
422 PRIMATE EVOLUTION Mack Henry/Visuals Unlimited Brain volume A primate’s brain volume is large relative to its body size. The complex behaviors of a
Molecular Insights into Human Brain Evolution PLOS
How Primate Brains Vary and Evolve Trends in Cognitive
Search text. Search type Research Explorer Website Staff directory. Alternatively, use our A–Z index
Understanding primate brain evolution
Genetic correlates of the evolving primate brain Request PDF
standing of primate brain evolution, we evaluate each of the major explanations and specify exactly what assumptions and potential limitations underlie each in turn.
Primate Evolution Evidence From the Fossil Record
The Evolution of the Primate Hominid and Human Brain
Analysis of Brain data for primates Why Prezi. The science Conversational presenting
Tactical deception in primates Behavioral and Brain
Chapter 16 Primate Evolution Mr. May’s Class
Evolution of the Primate Brain Size Is Just a Start
Throughout mammalian and primate evolution, there has been a gradual increase in brain size, superimposed with “spikes” of fast growth such as the tripling in human brain size that occurred about 1.5 million years ago, 4 million years after the human lineage diverged from that of the great apes.
Understanding Vertebrate Brain Evolution OUP Academic
external morphology of the primate brain Download eBook
as explanations for the evolution of enhanced brain size in primates (1, 4–6, 44, 45), so these authors would predict a positive relationship between relative brain size (specifically,
Evolution of the human brain Stories yourgenome.org
or occurred earlier in primate evolution is still unclear. Here we annotated CREs in several distinct anatomical regions . of adult brain tissue from human, rhesus macaque and chimpanzee. We found that the overall positional conservation of CREs is high, but observed differences in their usage. Furthermore, we show that most regulatory changes occurred before the divergence of human and
Genetic correlates of the evolving primate brain Request PDF
Primate Brain Evolution SpringerLink
development of a brain uniquely large for a primate, with disproportionate enlargement of association areas (Deacon, 1990). Humans suffer from this in two ways.
The Evolution of the Primate Hominid and Human Brain
Understanding primate brain evolution CORE
Tactical deception in primates Behavioral and Brain
standing of primate brain evolution, we evaluate each of the major explanations and specify exactly what assumptions and potential limitations underlie each in turn.
RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Reconstructing the ups and
evolution of the primate brain from neuron to behavior progress in brain research Download Book Evolution Of The Primate Brain From Neuron To Behavior Progress In Brain Research in PDF format. You can Read Online Evolution Of The Primate Brain From Neuron To Behavior Progress In Brain Research here in PDF, EPUB, Mobi or Docx formats.
How Primate Brains Vary and Evolve Trends in Cognitive
Evolution of the Size and Functional Areas of the Human Brain
Jerison, H. J. (1991 b) Brain size and the evolution of mind. The 59th James Arthur lecture on the evolution of the human brain . American Museum of Natural History .
Primate study offers clues to evolution of speech
Analysis of Brain data for primates Why Prezi. The science Conversational presenting
Neocortex Wikipedia
Genetic correlates of the evolving primate brain
3. Primate brain evolution revisited. In the light of these new findings, we have undertaken new analyses of the primate data, in order to be able to evaluate in greater depth the relationships between primate brain size and species-specific behavioural, ecological and life-history characteristics.
Understanding primate brain evolution Research Explorer
Social intelligence innovation and enhanced brain size
27/03/2014 · The similarity in brain design among primates, including humans, indicates that brain systems among related species are internally constrained and that the primate brain could only evolve within the context of a limited number of potential forms. It means that internal factors of brain design may be the primary determinants constraining the evolution of the brain and that geometric …
Why are there so many explanations for primate brain
Brain maps great and small lessons from comparative
We present a detailed reanalysis of the comparative brain data for primates, and develop a model using path analysis that seeks to present the coevolution of primate brain (neocortex) and sociality within a broader ecological and life-history framework.
external morphology of the primate brain Download eBook
27/03/2014 · The similarity in brain design among primates, including humans, indicates that brain systems among related species are internally constrained and that the primate brain could only evolve within the context of a limited number of potential forms. It means that internal factors of brain design may be the primary determinants constraining the evolution of the brain and that geometric …
Social intelligence innovation and enhanced brain size
are possible or likely requires understanding as much as we can about how brain struc-ture relates to behavioral variation. Unrav- eling the story of human evolution requires research in each of these areas: (a) general patterns of brain evolution, (b) compara-tive assessment of brain anatomy across species, (c) the fossil history of human-brain evolution, and (d) brain structure/function
Primate Vocal Communication A Useful Tool for
Evolution of the human brain Stories yourgenome.org
Social brain volume is associated with in-degree social network size among older adults. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, Vol. 285, Issue. 1871, p. 20172708. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, Vol. 285, Issue. 1871, p. 20172708.
Human and NonHuman Primate Brains Are They Allometrically
The human brain, in all its staggering complexity, is the product of millions of years of evolution. The brain has undergone some remarkable changes through its evolution. The most primitive brains are little more than clusters of cells bunched together at the front of an organism. These cells
Evolution of the Primate Brain Size Is Just a Start
Primate cognition from ‘what now?’ to ‘what if?’
Neocortex Wikipedia
The evolution of brain size and complexity in the Order Primates has been widely regarded as the hallmark of primate evolutionary history. Despite their importance to our understanding of primate evolution, the relationship between sexual selection and the evolutionary development of brain size is not well studied. The present research examines the evolutionary relationship between brain size
Human Evolution Cengage
Primate Brain Evolution SpringerLink
26/08/2016 · primate disease models for understanding the pathological mechanisms of brain disorders and for developing new approaches to effective treatment. However, we also emphasize that primate genetic models have great potential to address many fundamental questions about brain function, providing an essential foundation for future progress in disease research. B. rain disorders: an unmet need. Brain
Comparative primate neuroimaging insights into human
Neocortex Wikipedia
Primate Evolution Evidence From the Fossil Record
The evolution of trichromatic vision in primates is also a prominent example of molecular evolution (Shyue et al., 1995, Zhou and Li, 1996). Humans, apes, and old-world monkeys are trichromatic because they have three opsin genes each of which detects light at a different wavelength.
Understanding Vertebrate Brain Evolution OUP Academic
Tactical deception in primates – Volume 11 Issue 2 – A. Whiten, R. W. Byrne Tactical deception occurs when an individual is able to use an “honest” act from his normal repertoire in a different context to mislead familiar individuals.
Understanding primate brain evolution susanne.shultz
How Primate Brains Vary and Evolve Trends in Cognitive
Primate Brain Evolution SpringerLink
Understanding basic primate dentition is important for two reasons. First, because of their extreme hardness, teeth are the most common fossilized remains found by pa- leoanthropologists. Second, dental morphology provides information on the diet of fossil primates. Our review focuses on dental development, tooth structure, and the kind and numbers of teeth found in primates. All primates …
Endocranial morphology of Palaeocene Plesiadapis
Understanding primate brain evolution CORE
standing of primate brain evolution, we evaluate each of the major explanations and specify exactly what assumptions and potential limitations underlie each in turn.
Evolution of the human brain Stories yourgenome.org
Understanding primate brain evolution CORE
COGNITION, CONSCIOUSNESS, AND CULTURE: UNDERSTANDING HUMAN COGNITION AND ITS GROUNDING IN A PRIMATE BRAIN STANISLAS DEHAENE One of the key outstanding scientific questions for the 21st century con-
PDF Evolution Of The Primate Brain From Neuron To Behavior
Understanding primate brain evolution ResearchGate
Understanding primate brain evolution. Dunbar RIM., Shultz S. We show that body size, basal metabolic rate and life history act as constraints on brain evolution and through this influence the coevolution of neocortex size and group size.
Understanding primate brain evolution Research Explorer
The neocortex, also called the neopallium and isocortex, is the part of the mammalian brain involved in higher-order brain functions such as sensory perception, cognition, generation of motor commands, spatial reasoning and language.
RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Reconstructing the ups and
An Overview of the Primates MSU Department of Anthropology
Epigenomic annotation of gene regulatory alterations
as explanations for the evolution of enhanced brain size in primates (1, 4–6, 44, 45), so these authors would predict a positive relationship between relative brain size (specifically,
Primate brain evolution Philosophical Transactions of
Three Views Of Primate Brain Evolution Download eBook
Brains Genes and Primates cell.com
Evolution of the Primate Brain: Size Is Just a Start From prefrontal white matter to squiggly surface grooves, our brain stands out. Posted Sep 21, 2018
Evolution of the Size and Functional Areas of the Human Brain
Understanding primate brain evolution. (Manchester
Human Evolution Cengage
Evidence for grades within the primate brain suggests that there may be quantitative, or even qualitative, differences between monkey and ape social cog- nition.
Comparative primate neuroimaging insights into human
In this chapter, we provide a brief overview of human evolution.We start with a discussion of Darwin and the theory of natural selection, move on to talk about primates, their social lives, and tool usage, before turning to a summary of what we know about human evolution.We talk about
Understanding primate brain evolution ResearchGate
standing of primate brain evolution, we evaluate each of the major explanations and specify exactly what assumptions and potential limitations underlie each in turn.
Evolution of Primate Cognition Radical Anthropology Group
Sexual selection and the evolution of brain size in primates.
Understanding Primate Brain Evolution by Jona Somaraju on
The neocortex, also called the neopallium and isocortex, is the part of the mammalian brain involved in higher-order brain functions such as sensory perception, cognition, generation of motor commands, spatial reasoning and language.
Primate Vocal Communication A Useful Tool for
Download three views of primate brain evolution or read online here in PDF or EPUB. Please click button to get three views of primate brain evolution book now. All books are in clear copy here, and all files are secure so don’t worry about it.
Sexual selection and the evolution of brain size in primates.
Understanding Primate Brain Evolution by Jona Somaraju on
In the quest for a scientific understanding of human nature, no topic is more important than the evolution of the special features of the human brain [1,2]. The fossil record shows that brain size approximately tripled over the last 2.5 million years of human evolution [3]; however, the fossil record cannot identify potential evolutionary
Evolution of the Primate Brain Size Is Just a Start
Seeking Synthesis The Integrative Problem in
Jerison, H. J. (1991 b) Brain size and the evolution of mind. The 59th James Arthur lecture on the evolution of the human brain . American Museum of Natural History .
No Brain Too Small BIOLOGY Demonstrate understanding of
Brains Genes and Primates cell.com
Evolution of the Primate Brain Is Bigger Better
record, promise to contribute to a more complete understanding of primate evolution. Evolution is a complex subject encompassing the history of life and its governing processes. Our understanding of evolution is based on interpretation of patterns of diversity, ecology, behavior, visible morphology, and invisible molecular structure that have changed and continue to change through time. The
Understanding primate brain evolution (pdf) Paperity
Evolution of the Size and Functional Areas of the Human Brain
Download [PDF] evolution of a primate ardhindie.com
The human brain, in all its staggering complexity, is the product of millions of years of evolution. The brain has undergone some remarkable changes through its evolution. The most primitive brains are little more than clusters of cells bunched together at the front of an organism. These cells
Evolutionary Neuroscience 1st Edition
Jerison, H. J. (1991 b) Brain size and the evolution of mind. The 59th James Arthur lecture on the evolution of the human brain . American Museum of Natural History .
Understanding primate brain evolution Citation formats
COGNITION CONSCIOUSNESS AND CULTURE UNDERSTANDING HUMAN
evolution of the primate brain from neuron to behavior progress in brain research Download Book Evolution Of The Primate Brain From Neuron To Behavior Progress In Brain Research in PDF format. You can Read Online Evolution Of The Primate Brain From Neuron To Behavior Progress In Brain Research here in PDF, EPUB, Mobi or Docx formats.
Genetic correlates of the evolving primate brain
Three Views Of Primate Brain Evolution Download eBook
We present a detailed reanalysis of the comparative brain data for primates, and develop a model using path analysis that seeks to present the coevolution of primate brain (neocortex) and
Primate cognition from ‘what now?’ to ‘what if?’
Understanding primate brain evolution Research Explorer
Evolution of the Primate Brain Size Is Just a Start
Studies of brain evolution tend to focus on differences across species rather than on variation within species. A new study measures and compares intraspecific variation in macaque and human brain anatomy to explore the effect that short-term diversity has on long-term evolution.
Download [PDF] evolution of a primate ardhindie.com
How Primate Brains Vary and Evolve Trends in Cognitive
Download three views of primate brain evolution or read online here in PDF or EPUB. Please click button to get three views of primate brain evolution book now. All books are in clear copy here, and all files are secure so don’t worry about it.
Understanding primate brain evolution. — PSY