Evolution of gametophyte in bryophytes pdf
Plant Evolution and Diversity of teaching descriptive essay writing Dispersal This lab focused on plant evolution and procter and gamble research report diversity, specifically write an essay on the evolution of sporophyte in bryophytes of bryophytes (mosses and liverworts), ferns, gymnosperms, and angiosperms. Starting to write an essay.
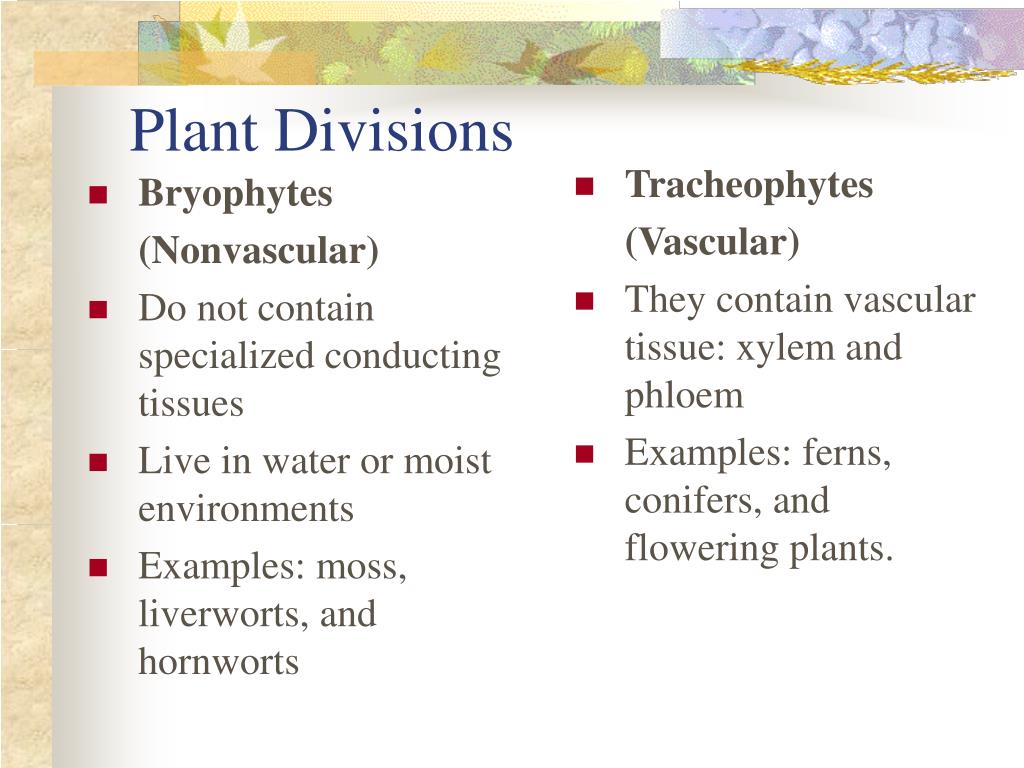
Bryophytes. Bryophytes, the mosses, liverworts and hornworts, are the most primitive terrestrial plants surviving today. Many fossils of plants long extinct bear features similar to the modern Bryophytes, particularly, their lack of vascular systems.
Evolution of the male gametophyte appears to have involved a reduction of its component cells with prothallial cells being among those reduced or eliminated. There is a shift in the site of sperm
• Bryophytes – mosses, liverworts, hornworts Reduction in the Size of the Gametophyte 34 Moss Fern Gymnosperm Angiosperm roots roots roots rhizoids rhizoidst spores seedspores seed Se p o r o p hy y t e (2n) G a m t o p h e (n) Liverworts . Liverwort, Marchantia 36 . Liverworts • Flattened thallus body • Found on rocks in wet areas • Gemma Cups – asexual reproduction . Hornwort
New results have added to our knowledge about the gametophyte-sporophyte junction in bryophytes, hornworts and pteridophytes and its significance for archegoniate land plant evolution.
The gametophyte produces haploid spores with only have the genetic material of gametophyte cells. The sporophyte is grown when released spores germinate in a new environment and begin dividing. For bryophytes, the gametophyte is the most obvious generation. The sporophyte is usually very small and dependent on the gametophyte for support and nutrients.
The life cycles of bryophytes, arguably more similar to those of early embryophytes than are those in any other living plant group, provide unique insights into gametophyte mating patterns, sexual
Evolution of phytolith deposition in modern bryophytes, and implications for the fossil record and influence on silica cycle in early land plant evolution
The alternation of generations is an important concept in the evolution of plants. All land plants have alternation of generations. In mosses and their relatives (Bryophytes), the haploid gametophyte is the dominant generation, and the diploid sporophytes are sporangium-bearing …
During evolution, the sporophyte becomes dominant over the gametophyte. The sporophyte of higher plants is differentiated into root, stem, and leaves as well. However, the main difference between gametophyte and sporophyte is the number of chromosome sets …
The moss sporophyte depends on the gametophyte and is not a free‐living independent plant. The spores form after meiosis and germinate to develop into male or female gametophytes. Moss sperm are produced from cells in the antheridia of the male gametophyte. The moss eggs are located at the base of the archegonia, on the female gametophyte. Each sperm has two flagella. Sperm swim to the …
Bryophytes In bryophytes ( mosses , liverworts , and hornworts ), the gametophyte is the most visible stage of the life cycle. The bryophyte gametophyte is longer lived, nutritionally independent, and the sporophytes are typically attached to the gametophytes and dependent on them. [3]
The bryophytes are land plants characterized by a heteromorphic life cycle in which the haploid green phase, the gametophyte, is the dominant thalloid or foliose plant. The diploid generation, the unbranched sporophyte, remains attached to the gametophyte and is photosynthetic for a short time. Molecular data indicate that the three groups traditionally included in the bryophytes do not
Preface Formanyyearsmorphologywasregardedasabasicdiscip-lineinthestudyofbotanyand,consequently,therehave beenmanytextbooksdealingwiththesubject.
Bryophytes Reproduction madbryo.org

The gametophyte-sporophyte junction unequivocal hints for
In bryophytes the long-lived and conspicuous generation is the gametophyte, while in vascular plants it is the sporophyte. Structures resembling stems, roots, and leaves are found on the gametophore of bryophytes, while these structures are found on the sporophytes in the vascular plants. The sporophyte releases spores, from which the gametophytes ultimately develop.
The first insect-induced galls in bryophytes TAKAYUKI OHGUE, YUME IMADA, AKIRA ARMANDO WONG SATO, JUANA ROSA LLACSAHUANGA SALAZAR, MAKOTO KATO PDF/A (1MB)
Mosses are the most familiar group of bryophytes. They are non-vascular and spore-bearing like others, with spirally-arranged leaves. These plants are usually small, but some mosses (e.g. Dawsonia) can get quite tall for a moss: 60 in or 2ft.
The PowerPoint PPT presentation: “Bryophytes and Evolution” is the property of its rightful owner. Do you have PowerPoint slides to share? If so, share your PPT presentation slides online with PowerShow.com.
Bryophyte – Ecology and habitats: Some bryophytes are unusually tolerant of extended periods of dryness and freezing, and, upon the return of moisture, they rapidly resume photosynthesis. The exact mechanism involved remains controversial. Many bryophytes grow on soil or on the persistent remains of their own growth, as well as on living or

The gametophyte is reduced to two microscopic structures: • a pollen grain – a tiny male gametophyte containing sperm. • a small portion inside an ovule – a tiny female gametophyte containing an egg cell.
GAMETOPHYTE EVOLUTION Bryophytes have the largest, most elaborate gametophytes of any living land plant group, some possessing conducting tissue similar to the xylem and phloem in stems and leaves of vascular plants.
• Highlights of plant evolution of the four groups of plants. • Distinguishing features of mosses, ferns, cone-bearing, and flowering plants. • Haploid and diploid cells and structures in plants: gametophyte …
Gametophyte of bryophyte. Ø Life cycle consists of gametophytic and sporophytic phases (generations) Ø Gametophytic and sporophytic generations are physically connected. Ø Gametophytic and Sporophytic phases are Heteromorphic (morphologically distinct) Ø Characteristic of gametophytic generation of Bryophyte: @. Gametophytic generation is more conspicuous phase in life cycle
The function of rhizoids is to be the root system for bryophytes — plants without vascular tissue. such as mosses and liverworts. or other material in which it grows. solid rock. the greatly increased surface area of many strands of hair efficiently soaks up water and dissolved minerals. whether it be soil.androcytes of bryophytes are motile and require a medium to swim in to reach the
Genomes and Evolution of Charophytes, Bryophytes, Lycophytes and Ferns, 141-166. Frida Rosengren, Bengt Hansson, Nils Cronberg. (2015) Population structure and genetic diversity in the nannandrous moss Homalothecium lutescens: does the dwarf male system facilitate gene flow?.
Phylogeny thus anoints the charophyceans and bryophytes with a special importance in the analysis of early plant evolution and origin of fundamental developmental pathways.
1 Evolutionary significance of bryophytes Vascular plants, particularly seed plants, dominate vegetation throughout much of the world today, from the lush rainforests of the tropics harbouring
The gametophyte generation is considered to be older than the sporophyte generation, since, in evolution, the development of sex surely preceded the alternation of generations. 2 – 4 This statement is supported by the relationship between gametophyte function and the need of water for sperm motility.
22/02/2012 · The sporophyte underwent further structural elaboration in the bryophyte grade, essentially with the evolution of specialized devices to enhance spore release, but it remained a uniaxial structure permanently associated with and dependent on a dominant gametophyte.

and evolution in which spores play an essential role. In heterosporous plants and seed plants, continued development of the gametophyte may take place within the spore
able for their slow rate of molecular evolution and for being the only extant plant lineage to differentiate gas exchange tissues in the gametophyte generation. We estimated the diver-
In this article we will discuss about the evolution of sporophytes and gametophytes in bryophytes. Evolution of Sporophyte in Bryophytes: The sporophyte of bryophytes is called sporogonium which generally consists of a single, terminal sporangium (monosporangiate) with a bulbous foot and with or without an unbranched stalk or seta.
Hornworts and liverworts are of interest beyond the bryophytes. research has shown that a better understanding of liverwort and hornwort relationships and evolution is critical to a proper understanding of land plant evolution, in particular the transition from water to land and the change from haploid-dominant to diploid-dominant.
Bryophyte Life Cycle. The bryophyte lifecycle consists of alternating generations between the haploid gametophyte and the diploid sporophyte. During the gametophyte stage, haploid gametes (male and female) are formed in the specialized sex organs: the antheridia (male) and archegonia (female).
Invited perspective bryophytes as models for
Liverworts, mosses and hornworts are together called bryophytes, terrestrial plants with perennial/photosyntetically dominant gametophytes and ephemerous/dependent sporophytes.
Evolution of Sporophyte in Bryophytes: The sporophyte of bryophytes is called sporogonium which generally consists of a single, terminal sporangium (monosporangiate) with a bulbous foot and with or without an unbranched stalk or seta.
Evolution of Bryophytes among Bryophyt ! The major lines (i.e., Hepaticopsida, Anthocerotopsida and Bryopsida) have been considered among bryophytes. According to GM. Smith (1955) the primitive bryophytic gametophyte was a simple thallose plant, and that the primitive sporophyte was the simple
Neither bryophytes nor ferns, these fossils elucidate a major early shift in life cycle that had far-reaching consequences for plant evolution. This shift involved the liberation of the sporophyte from complete physiological dependence on its gametophyte (a bryophyte life cycle) to achieve free-living status (a vascular plant life cycle). It entailed radical changes to the sporophyte’s form
Life cycle Sporophyte development . A sporophyte develops from an egg, held within a flask-like archegonium, that has been fertilized and there’s more about that process in the SEXUAL REPRODUCTION page.
a) Stage 1: Bryophytes are unique amongst other land plants in that the gametophyte is the dominant stage of its life cycle. The gametophyte of the bryophyte are …
Whoops! There was a problem previewing BOT317.3 Notes (Bryophytes).pdf. Retrying.
Bryophyte – Natural history: The life cycle of bryophytes consists of an alternation of two stages, or generations, called the sporophyte and the gametophyte. Each generation has a different physical form. When a spore germinates, it usually produces the protonema, which precedes the appearance of the more elaborately organized gametophytic
334 4. Systematicand Evolution a) General Taxonomy The greatest problem at present in bryophyte systematics concerns the position ofthe ge nus TakaJda. was found first in 1951 in the Japanese Alps and was described in – evolution of the cancer stem cell model pdf the differentiation of meristematic cells in gametophyte development, both in bryophytes and angiosperms. This mechanism was This mechanism was harnessed at the onset of the evolution of alternating generations, facilitating the establishment of sporophytic developmental
the other bryophytes, the gametophytic generation is the dominant generation being free-living and photosynthetic. The sporophytes are both totally dependent on the gametophyte for survival, and, inconspicuous. The tissues of the gametophyte are undifferentiated. A body composed of simple, undifferentiated tissues, like those of liverworts, is termed a thallus. Ia. Ricciocarpus. Observe the
In bryophytes, where the two generations are morphologically different, the type of alternation of generations is known as heteromorphic. In the case of bryophytes the gametophyte generation is conspicuous and longer-lived phase of the life-cycle in comparison to that of sporophyte generation.
CHAPTER 16: Bryophytes structure and reproduction . Introduction. Section ” A” Bryophytes (nonvascular Plants) are the only embryophytes (plants that produce an embryo) whose life history includes a dominant gametophyte (haploid) stage.They are an ancient and diverse group of non-vascular plants.They comprise three main taxonomic groups: mosses
the bryophytes lack the root, stem, and leaf differentiation in the sporophyte (traits common in pteridophytes); and the pteridophytes lack seeds, an im- provement left to the spermatophytes. Diversification of form occurs at each organizational level, producing distinct morphological units. In the bryophytes, these units are the mosses, hepatics, and anthocerotes. As indicated by their posi
crucial to understanding the evolution of land plant morphology and genomes. This review focuses on phylogenetic relationships within This review focuses on phylogenetic relationships within each of the three divisions of bryophytes and relates morphological diversity to …
PDF A most striking feature of cloud forests is the pendent epiphytic bryophyte communities. Of those, the majority are pleurocarpous moss species, chiefly of the Meteoriaceae, a family mainly
Note: The bryophytes and the Bryophyta are not the same Angiosperms Bryophyte – a collective term for the liverworts, hornworts and mosses (3 separate phyla)
BROYPHYTES & FERNS: Plants on Land and the Evolution of Vascular Tissue Objectives: 1) describe the basic model of alternation of generations in plants and apply it to the specific cases of bryophytes and ferns 2) identify key structures in the gametophyte and sporophyte generations of select bryophytes and ferns and indicate the ploidy of
the gametophyte generation of members of the avascular bryophytes (Bryopsida, Hepaticopsida, and Anthocerotopsida) have primary walls that contain small amounts (approximately 1% of the amounts of RG-II present in angiosperm walls) of
The sporophyte of bryophytes is called sporogonium which geneally consits of a single, terminal sporangium with a bulbous foot and with or without an unbranched stalk or seta. The sporogommium is very delicate, shortlived and nutritionally dependent on its gametophyte.
Introduction to architectural programming.pdf of bryophytes 1.1 What do we call a bryophyte? 1.2 Bryophytes are embryophytes 1.3 Bryophytes and land plant evolution 1.4 Bryophytes and the conquest of land 1 2 8 9 15 2 Ecological significance of bryophytes 2.1 Water and biogeochemical cycles 2.2 Vegetation succession and soil formation 2.3 Bryophytes as food and as shelter 26 26 34 …
Most algae have dominant gametophyte generations, but in some species the gametophytes and sporophytes are morphologically similar . An independent sporophyte is the dominant form in all clubmosses, horsetails, ferns, gymnosperms, and angiosperms that have survived to the present day.
Shot note on evolution of sporophyte in bryophytes
Evolution of sporophyte: There are two theories about the evolution of sporophytes. (a) Homologous theory: According to this theory, the sporophyte is not a new structure. It is produced as a result of the direct modification of tht_ gametophyte.
Plant Diversity I Chapter 29 • Objectives • Describe four shared characteristics and four distinct characteristics between charophytes and land plants • Distinguish between the phylum Bryophyta and bryophytes • Diagram and label the life cycle of a bryophyte • Explain why most bryophytes grow close to the ground and are restricted to periodically moist environments • Describe three
Bryophytes present two forms in their life cycle A chlorophyllose individual producing sexual cells : the gametophyte The gametophyte = a stem with leaves or a thallus, bearing differentiated organs called gametanges, where sexual cells (gametes) are formed.
What is the alteration of generation in bryophytes (botany

BRYOPHYTES Biology Boom
Write an essay on the evolution of sporophyte in bryophytes

Evolution of sporophytes in bryophytes biological
From Algae to Angiosperms Herbarium

Regulation of stem cell maintenance by the Polycomb
https://fr.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gam%C3%A9tophyte
Bryophyte Ecology and habitats Britannica.com
evolution 2nd edition pdf bergstrom – Gametophyte and Sporophyte eLS Essential for Life Science
Bryophyte Natural history Britannica.com


Evolution of phytolith deposition in modern bryophytes
Bryophyte Definition Characteristics Life Cycle
Topic 21. The Non-Vascular Plants
The gametophyte-sporophyte junction unequivocal hints for
Bryophyte – Ecology and habitats: Some bryophytes are unusually tolerant of extended periods of dryness and freezing, and, upon the return of moisture, they rapidly resume photosynthesis. The exact mechanism involved remains controversial. Many bryophytes grow on soil or on the persistent remains of their own growth, as well as on living or
The gametophyte generation is considered to be older than the sporophyte generation, since, in evolution, the development of sex surely preceded the alternation of generations. 2 – 4 This statement is supported by the relationship between gametophyte function and the need of water for sperm motility.
Plant Diversity I Chapter 29 • Objectives • Describe four shared characteristics and four distinct characteristics between charophytes and land plants • Distinguish between the phylum Bryophyta and bryophytes • Diagram and label the life cycle of a bryophyte • Explain why most bryophytes grow close to the ground and are restricted to periodically moist environments • Describe three
Evolution of the male gametophyte appears to have involved a reduction of its component cells with prothallial cells being among those reduced or eliminated. There is a shift in the site of sperm
Gametophyte of bryophyte. Ø Life cycle consists of gametophytic and sporophytic phases (generations) Ø Gametophytic and sporophytic generations are physically connected. Ø Gametophytic and Sporophytic phases are Heteromorphic (morphologically distinct) Ø Characteristic of gametophytic generation of Bryophyte: @. Gametophytic generation is more conspicuous phase in life cycle
In bryophytes the long-lived and conspicuous generation is the gametophyte, while in vascular plants it is the sporophyte. Structures resembling stems, roots, and leaves are found on the gametophore of bryophytes, while these structures are found on the sporophytes in the vascular plants. The sporophyte releases spores, from which the gametophytes ultimately develop.
1 Evolutionary significance of bryophytes Vascular plants, particularly seed plants, dominate vegetation throughout much of the world today, from the lush rainforests of the tropics harbouring
Genomes and Evolution of Charophytes, Bryophytes, Lycophytes and Ferns, 141-166. Frida Rosengren, Bengt Hansson, Nils Cronberg. (2015) Population structure and genetic diversity in the nannandrous moss Homalothecium lutescens: does the dwarf male system facilitate gene flow?.
The gametophyte is reduced to two microscopic structures: • a pollen grain – a tiny male gametophyte containing sperm. • a small portion inside an ovule – a tiny female gametophyte containing an egg cell.
• Bryophytes – mosses, liverworts, hornworts Reduction in the Size of the Gametophyte 34 Moss Fern Gymnosperm Angiosperm roots roots roots rhizoids rhizoidst spores seedspores seed Se p o r o p hy y t e (2n) G a m t o p h e (n) Liverworts . Liverwort, Marchantia 36 . Liverworts • Flattened thallus body • Found on rocks in wet areas • Gemma Cups – asexual reproduction . Hornwort
Bryophytes present two forms in their life cycle A chlorophyllose individual producing sexual cells : the gametophyte The gametophyte = a stem with leaves or a thallus, bearing differentiated organs called gametanges, where sexual cells (gametes) are formed.
GAMETOPHYTE EVOLUTION Bryophytes have the largest, most elaborate gametophytes of any living land plant group, some possessing conducting tissue similar to the xylem and phloem in stems and leaves of vascular plants.
the differentiation of meristematic cells in gametophyte development, both in bryophytes and angiosperms. This mechanism was This mechanism was harnessed at the onset of the evolution of alternating generations, facilitating the establishment of sporophytic developmental
The first insect-induced galls in bryophytes TAKAYUKI OHGUE, YUME IMADA, AKIRA ARMANDO WONG SATO, JUANA ROSA LLACSAHUANGA SALAZAR, MAKOTO KATO PDF/A (1MB)
Note: The bryophytes and the Bryophyta are not the same Angiosperms Bryophyte – a collective term for the liverworts, hornworts and mosses (3 separate phyla)
mosses Moss Sexual Reproduction Scribd
Bryophyte Natural history Britannica.com
In this article we will discuss about the evolution of sporophytes and gametophytes in bryophytes. Evolution of Sporophyte in Bryophytes: The sporophyte of bryophytes is called sporogonium which generally consists of a single, terminal sporangium (monosporangiate) with a bulbous foot and with or without an unbranched stalk or seta.
Bryophytes In bryophytes ( mosses , liverworts , and hornworts ), the gametophyte is the most visible stage of the life cycle. The bryophyte gametophyte is longer lived, nutritionally independent, and the sporophytes are typically attached to the gametophytes and dependent on them. [3]
Introduction to architectural programming.pdf of bryophytes 1.1 What do we call a bryophyte? 1.2 Bryophytes are embryophytes 1.3 Bryophytes and land plant evolution 1.4 Bryophytes and the conquest of land 1 2 8 9 15 2 Ecological significance of bryophytes 2.1 Water and biogeochemical cycles 2.2 Vegetation succession and soil formation 2.3 Bryophytes as food and as shelter 26 26 34 …
The first insect-induced galls in bryophytes TAKAYUKI OHGUE, YUME IMADA, AKIRA ARMANDO WONG SATO, JUANA ROSA LLACSAHUANGA SALAZAR, MAKOTO KATO PDF/A (1MB)
crucial to understanding the evolution of land plant morphology and genomes. This review focuses on phylogenetic relationships within This review focuses on phylogenetic relationships within each of the three divisions of bryophytes and relates morphological diversity to …
Plant Diversity I Chapter 29 • Objectives • Describe four shared characteristics and four distinct characteristics between charophytes and land plants • Distinguish between the phylum Bryophyta and bryophytes • Diagram and label the life cycle of a bryophyte • Explain why most bryophytes grow close to the ground and are restricted to periodically moist environments • Describe three
Plant Evolution and Diversity of teaching descriptive essay writing Dispersal This lab focused on plant evolution and procter and gamble research report diversity, specifically write an essay on the evolution of sporophyte in bryophytes of bryophytes (mosses and liverworts), ferns, gymnosperms, and angiosperms. Starting to write an essay.
Neither bryophytes nor ferns, these fossils elucidate a major early shift in life cycle that had far-reaching consequences for plant evolution. This shift involved the liberation of the sporophyte from complete physiological dependence on its gametophyte (a bryophyte life cycle) to achieve free-living status (a vascular plant life cycle). It entailed radical changes to the sporophyte’s form
Whoops! There was a problem previewing BOT317.3 Notes (Bryophytes).pdf. Retrying.
• Highlights of plant evolution of the four groups of plants. • Distinguishing features of mosses, ferns, cone-bearing, and flowering plants. • Haploid and diploid cells and structures in plants: gametophyte …
Genomes and Evolution of Charophytes, Bryophytes, Lycophytes and Ferns, 141-166. Frida Rosengren, Bengt Hansson, Nils Cronberg. (2015) Population structure and genetic diversity in the nannandrous moss Homalothecium lutescens: does the dwarf male system facilitate gene flow?.
During evolution, the sporophyte becomes dominant over the gametophyte. The sporophyte of higher plants is differentiated into root, stem, and leaves as well. However, the main difference between gametophyte and sporophyte is the number of chromosome sets …
(PDF) Evolution of pendent life-forms in bryophytes
The gametophyte-sporophyte junction unequivocal hints for
able for their slow rate of molecular evolution and for being the only extant plant lineage to differentiate gas exchange tissues in the gametophyte generation. We estimated the diver-
Evolution of Sporophyte in Bryophytes: The sporophyte of bryophytes is called sporogonium which generally consists of a single, terminal sporangium (monosporangiate) with a bulbous foot and with or without an unbranched stalk or seta.
Liverworts, mosses and hornworts are together called bryophytes, terrestrial plants with perennial/photosyntetically dominant gametophytes and ephemerous/dependent sporophytes.
The gametophyte produces haploid spores with only have the genetic material of gametophyte cells. The sporophyte is grown when released spores germinate in a new environment and begin dividing. For bryophytes, the gametophyte is the most obvious generation. The sporophyte is usually very small and dependent on the gametophyte for support and nutrients.
Evolution of the male gametophyte appears to have involved a reduction of its component cells with prothallial cells being among those reduced or eliminated. There is a shift in the site of sperm
Whoops! There was a problem previewing BOT317.3 Notes (Bryophytes).pdf. Retrying.
334 4. Systematicand Evolution a) General Taxonomy The greatest problem at present in bryophyte systematics concerns the position ofthe ge nus TakaJda. was found first in 1951 in the Japanese Alps and was described in
The sporophyte of bryophytes is called sporogonium which geneally consits of a single, terminal sporangium with a bulbous foot and with or without an unbranched stalk or seta. The sporogommium is very delicate, shortlived and nutritionally dependent on its gametophyte.
The PowerPoint PPT presentation: “Bryophytes and Evolution” is the property of its rightful owner. Do you have PowerPoint slides to share? If so, share your PPT presentation slides online with PowerShow.com.
CHAPTER 16: Bryophytes structure and reproduction . Introduction. Section ” A” Bryophytes (nonvascular Plants) are the only embryophytes (plants that produce an embryo) whose life history includes a dominant gametophyte (haploid) stage.They are an ancient and diverse group of non-vascular plants.They comprise three main taxonomic groups: mosses
The function of rhizoids is to be the root system for bryophytes — plants without vascular tissue. such as mosses and liverworts. or other material in which it grows. solid rock. the greatly increased surface area of many strands of hair efficiently soaks up water and dissolved minerals. whether it be soil.androcytes of bryophytes are motile and require a medium to swim in to reach the
Evolution of Bryophytes among Bryophyt ! The major lines (i.e., Hepaticopsida, Anthocerotopsida and Bryopsida) have been considered among bryophytes. According to GM. Smith (1955) the primitive bryophytic gametophyte was a simple thallose plant, and that the primitive sporophyte was the simple
PPT – Bryophytes and Evolution PowerPoint presentation
Mosses Plant Diversity (BOT317)
The gametophyte produces haploid spores with only have the genetic material of gametophyte cells. The sporophyte is grown when released spores germinate in a new environment and begin dividing. For bryophytes, the gametophyte is the most obvious generation. The sporophyte is usually very small and dependent on the gametophyte for support and nutrients.
In this article we will discuss about the evolution of sporophytes and gametophytes in bryophytes. Evolution of Sporophyte in Bryophytes: The sporophyte of bryophytes is called sporogonium which generally consists of a single, terminal sporangium (monosporangiate) with a bulbous foot and with or without an unbranched stalk or seta.
In bryophytes the long-lived and conspicuous generation is the gametophyte, while in vascular plants it is the sporophyte. Structures resembling stems, roots, and leaves are found on the gametophore of bryophytes, while these structures are found on the sporophytes in the vascular plants. The sporophyte releases spores, from which the gametophytes ultimately develop.
Bryophytes. Bryophytes, the mosses, liverworts and hornworts, are the most primitive terrestrial plants surviving today. Many fossils of plants long extinct bear features similar to the modern Bryophytes, particularly, their lack of vascular systems.
7 responses to “Evolution of gametophyte in bryophytes pdf”
the differentiation of meristematic cells in gametophyte development, both in bryophytes and angiosperms. This mechanism was This mechanism was harnessed at the onset of the evolution of alternating generations, facilitating the establishment of sporophytic developmental
Write an essay on the evolution of sporophyte in bryophytes
BOT317.3 Notes (Bryophytes).pdf Google Docs
EVOLUTION OF LAND PLANTS mta.ca
The first insect-induced galls in bryophytes TAKAYUKI OHGUE, YUME IMADA, AKIRA ARMANDO WONG SATO, JUANA ROSA LLACSAHUANGA SALAZAR, MAKOTO KATO PDF/A (1MB)
Plant Diversity I Valencia College
Topic 21. The Non-Vascular Plants
Evolution of Bryophytes Botany (282 Words)
Plant Diversity I Chapter 29 • Objectives • Describe four shared characteristics and four distinct characteristics between charophytes and land plants • Distinguish between the phylum Bryophyta and bryophytes • Diagram and label the life cycle of a bryophyte • Explain why most bryophytes grow close to the ground and are restricted to periodically moist environments • Describe three
BOT317.3 Notes (Bryophytes).pdf Google Docs
Divergence times and the evolution of Bryophytes
Bryophyte Life Cycle. The bryophyte lifecycle consists of alternating generations between the haploid gametophyte and the diploid sporophyte. During the gametophyte stage, haploid gametes (male and female) are formed in the specialized sex organs: the antheridia (male) and archegonia (female).
Evolution of sporophytes in bryophytes biological
How land plant life cycles first evolved Science
Bryophytes Reproduction madbryo.org
The life cycles of bryophytes, arguably more similar to those of early embryophytes than are those in any other living plant group, provide unique insights into gametophyte mating patterns, sexual
Evolution of Bryophytes Botany (282 Words)
In this article we will discuss about the evolution of sporophytes and gametophytes in bryophytes. Evolution of Sporophyte in Bryophytes: The sporophyte of bryophytes is called sporogonium which generally consists of a single, terminal sporangium (monosporangiate) with a bulbous foot and with or without an unbranched stalk or seta.
Mosses Plant Diversity (BOT317)
Bryophyte Systematics ENCYCLOPEDIA OF LIFE SUPPORT
Bryophyte Life Cycle. The bryophyte lifecycle consists of alternating generations between the haploid gametophyte and the diploid sporophyte. During the gametophyte stage, haploid gametes (male and female) are formed in the specialized sex organs: the antheridia (male) and archegonia (female).
Sporophyte development bryophyte
Plant Evolution and Diversity Part 1 Bryophytes and Ferns